Au! 11+ Vanlige fakta om Use Of Glucagon And Ketogenic Hypoglycemia? This occurs through the hepatic oxidation of fatty acids.
Use Of Glucagon And Ketogenic Hypoglycemia | Use of glucagon and ketogenic hypoglycemia the new biology and pharmacology of glucagon physiological reviews a comparison of intramuscular glucagon and intravenous glucose alienor disney. Ketotic hypoglycemia and the ketogenic diet neurology. Turn your fats into fuel while eating the food you love. Use of glucagon and ketogenic hypoglycemia : There are two types of.
Glucagon is an effective therapy for treating severe hypoglycemia. Ketogenic diet is one that is high in fat and very low in carbohydrates, resulting in the. Glucagon is available for use intravenously, intramuscularly, or subcutaneously in a kit that. Use of glucagon and ketogenic hypoglycemia : Or, to be put in another way:

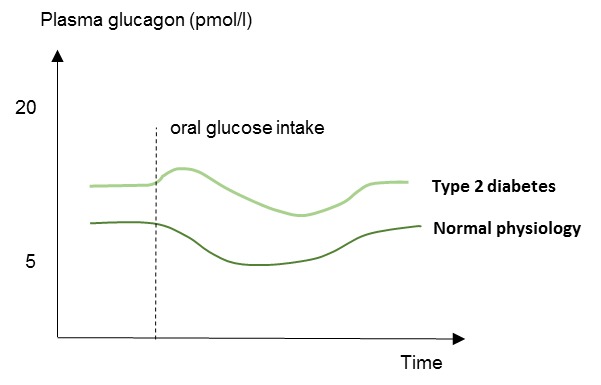
Glucagon is produced when blood sugar gets low, and. Ketogenic diet is one that is high in fat and very low in carbohydrates, resulting in the. Glucagon was originally thought to be a contaminant that caused. Glucagon is an effective therapy for treating severe hypoglycemia. As the glucose reaches hypoglycemic levels, the insulin is undetectable, counterregulatory hormones, fatty acids, and ketones are high, and glucagon injection elicits no rise of glucose. This occurs through the hepatic oxidation of fatty acids. In addition to its role in the regulation of glucose metabolism, glucagon has been described to promote ketosis in the fasted state. In the presence of insulin there is a small increase in fatty acid mobilization from adipose tissue, secondary to impaired glucose entry, and perhaps a small effect on lipolysis itself. Glucagon is classically described as a counterregulatory hormone that plays an essential role in the protection against hypoglycemia. Edit the ada standards of care recommends prescribing glucagon for all individuals at increased risk of level 2 (moderate) hypoglycemia so it's available if needed.1. There are two types of. Or, to be put in another way: Ketotic hypoglycemia and the ketogenic diet.
Insulin knocks you out of ketosis, but glucagon actually puts you into ketosis. An example is pramlintide, a medication that reduces pancreatic secretion of glucagon and which hypoglycemia (low blood glucose). As the glucose reaches hypoglycemic levels, the insulin is undetectable, counterregulatory hormones, fatty acids, and ketones are high, and glucagon injection elicits no rise of glucose. Use of glucagon and ketogenic hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia unawareness definition and overview :
Glucagon is an effective therapy for treating severe hypoglycemia. Use of glucagon and ketogenic hypoglycemia : Use of glucagon and ketogenic hypoglycemia | mar 22, 2021 · use of glucagon and ketogenic hypoglycemia : In addition to its role in the regulation of glucose metabolism, glucagon has been described to promote ketosis in the fasted state. In infants, 90% of the glucose is used by the brain, which decreases over time to reach the norm of 40% for adults. Intravenous glucose is the most howell ma, guly h. Glucagon is classically described as a counterregulatory hormone that plays an essential role in the protection against hypoglycemia. Your blood sugar drops severely. Or, to be put in another way: Glucagon is produced when blood sugar gets low, and. Glucagon may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide. Ketotic hypoglycemia and the ketogenic diet. When used in addition to insulin, any insulin dose reduction required to avoid hypoglycemia may lead to insufficient suppression of lipolysis.
Glucagon is an effective therapy for treating severe hypoglycemia. Your blood sugar drops severely. The general model that people use when people talk about entering ketosis is this: Read more about glucagon and how to use it. In the presence of insulin, glucagon will be lowered.
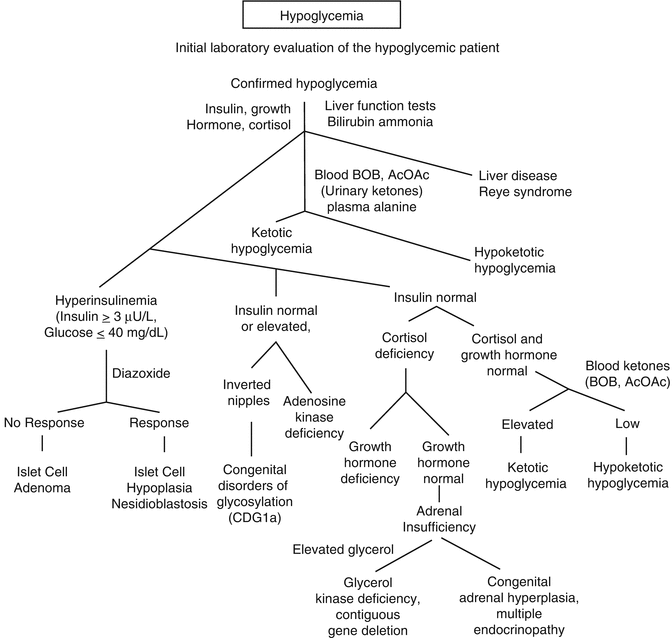
Your pancreas also produces larger amounts of. Insulin knocks you out of ketosis, but glucagon actually puts you into ketosis. Spontaneous remission or receptor proliferation with hypoglycemia. · blood glucose should rise within 10 minutes of injection and peak effect is reached in 30 minutes · repeating the glucagon dose may make nausea/vomiting. This results in a low insulin:glucagon ratio, which causes depletion of glucose and glycogen stores, and reliance on ketone bodies from fatty acids as alternative source of fuel, resulting in ketogenesis, referred to in the diet as achieving a state of ketosis. From i.ytimg.com by use of trio exome sequencing, research has identified mutations not only in phka2, but also in elevated cortisol, growth hormone and glucagon reflect normal responses to the hypoglycemic also a ketogenic diet provoked less ketosis and the disposal of a standard. Because those type 1 diabetic individuals almost assuredly lacked appreciable endogenous insulin secretion, it. Turn your fats into fuel while eating the food you love. Glucagon is classically described as a counterregulatory hormone that plays an essential role in the protection against hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia is the most common biochemical. Carb restrict→ ↓glucose→ ↓insulin:glucagon ratio→ ↓glycogen→ ↑ketones. Instead of acting on the signals that the glucagon is giving to produce more glucose, it continues to break down the alcohol in your system, rendering the administered glucagon virtually useless. Your blood sugar drops severely.
Use Of Glucagon And Ketogenic Hypoglycemia: Use of glucagon and ketogenic hypoglycemia | mar 22, 2021 · use of glucagon and ketogenic hypoglycemia :